The transition from conventional fuel vehicles to Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) marks a pivotal evolution in the automotive industry. This evolution demands continuous innovation in the manufacturing processes of BEVs. In this blog, we'll dive into the intricacies, features, and challenges of two stations engineered by SK for assembly lines, highlighting the crucial role of engineered excellence and precision.
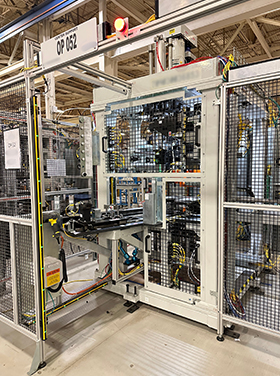
OP 52 Station
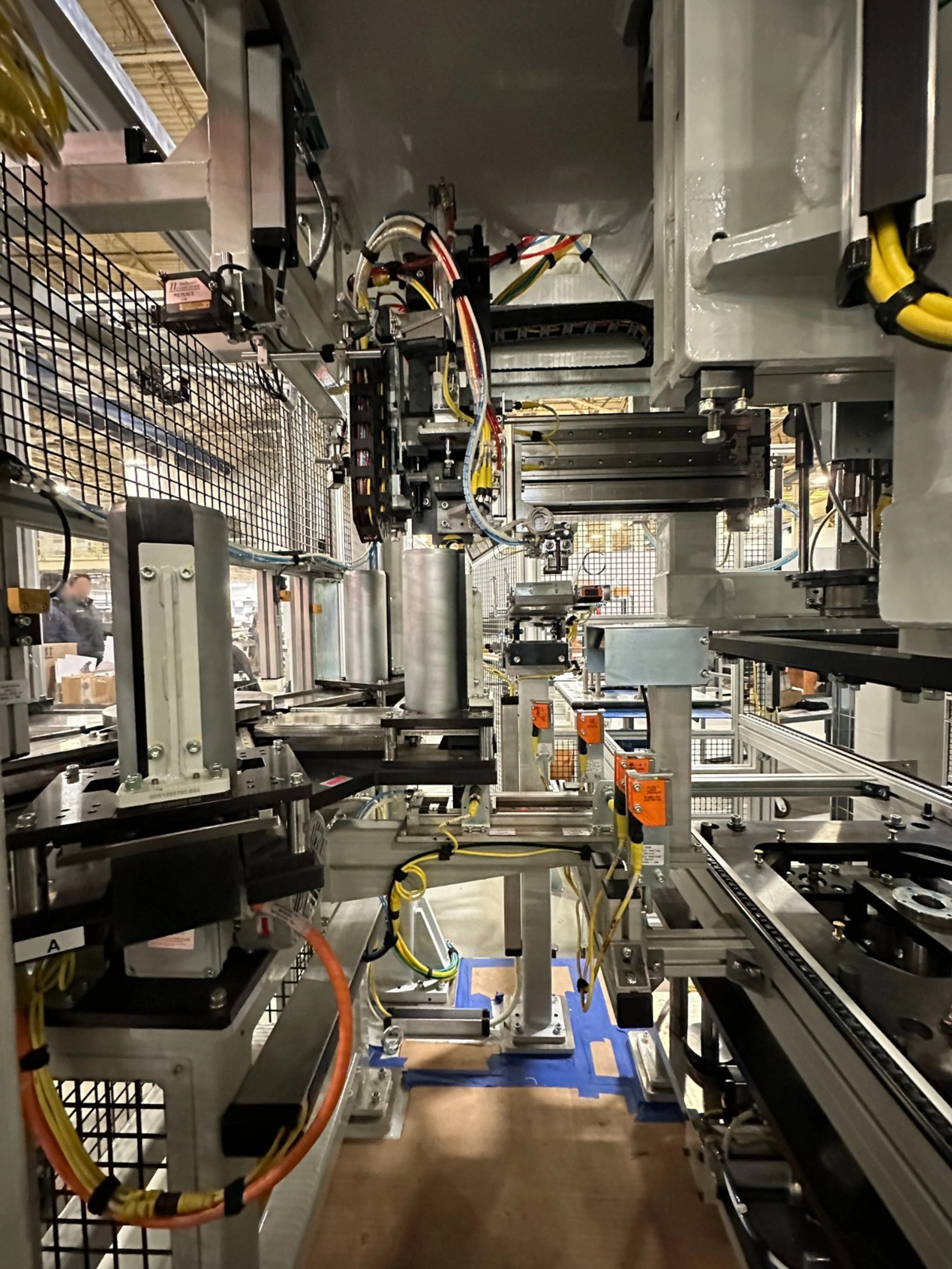
The objective of this station was to design and manufacture a Semi-Automatic Machine for the Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) Center Support with an 11mm Transfer Axis Change. The station was designed to press the bearing onto the center support and install a transfer axis from the bottom end. It was meticulously crafted to fulfill its functions, while also encompassing a versatile approach. It features two nests: one for loading the transfer axis and the other for an operator to load the bearing. The station is equipped with press tooling that inserts the bearing into the center support and the center support and bearing into the transfer axis shaft. Additionally, a gripper unit is included for picking the pallet's center support from the conveyor.
How Does It Work?
The operator loads the transfer axis and bearing into respective nests and hits the cycle start button. Tooling on a servo slide moves the transfer axis to the press position, and the bearing shuttles to the pick position. Using an additional horizontal servo slide, the gripper takes the center support from the pallet and places it on a plate with locating pins at the press position above the transfer axis.
The press tooling picks the bearing and places it in the center support. There is a backup tooling that actuates from the bottom of the station. The press unit inserts the bearing into the center support, and then the bearing and center support to the shaft of the transfer axis.
The station has sensors in the bearing nest to detect when the bearing has been loaded, when the transfer axis is loaded into its nest, and when the center support has been positioned for the press/insert operation.
Throughout this project, some challenges emerged. Firstly, there was the task of designing the station to facilitate a multitude of motions while ensuring that station operations could be completed within the specified cycle time. Additionally, a challenge presented itself in configuring the station to integrate with a 50Kn press, without encountering any operational issues. Perhaps the most significant challenge was the necessity to concurrently design and manufacture for two distinct locations within a tight timeframe. However, despite the obstacles, the SK team managed to overcome them, and Station OP 52 was successfully created. As a result, the customer expressed great satisfaction with the outcomes.
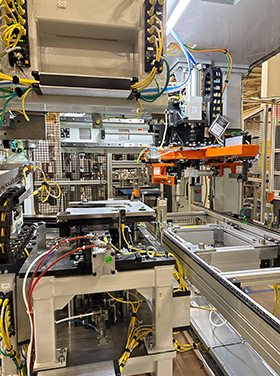
OP 54 Station
As opposed to the initial station, which was intended for a semi-automatic machine, station OP 54 was designed and produced specifically to be used in a fully automatic machine that is part of the Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) Central Support.
This station includes a snap ring within the central support assembly to secure the bearing previously installed. Products assembled at station OP 52 move along the conveyor belt to station OP 54. Additionally, the station features six snap ring magazines with a stack of snap rings mounted on the rotary indexer. This equipment includes a gripper tooling that is used to pick up the snap ring and place it in the pressing tooling. The press tooling, equipped with a 12 Kn press, precisely inserts the snap ring into the product to ensure quality and precision, a verification head carefully inspects the snap ring's placement within the product at every step of the assembly process.
How Does It Work?
The process at station OP 54 initiates when the operator initiates the station cycle. The process starts with the slicing unit dropping the snap ring from the snap ring magazine into the snap ring shuttle tooling. Using the shuttle tooling, the gripper selects the snap ring and places it inside the funnel unit. Next, the pressing tool guides the snap ring into a funnel, inserts it into the product, and presses it securely. Throughout this process, a backup tool engages with the product during the snap ring pressing operation. Once installed, the verification head tooling's LVDT sensors measure the snap ring ID to ensure it is seated correctly. Furthermore, integrated sensors verify the presence of the snap ring in the tooling and verify correct insertion into the product ensuring the integrity and quality of the process.
Similar to the challenges faced during the development of Station 0P52, this station encountered comparable obstacles. However, these challenges were successfully overcome.